Two dimensional Array in C language
Table of Contents
Knowledge Area
- What is Array
- Type of Arrays
- Declaration of two dimensional Array
- Two dimensional Array Initialization
- Two dimensional Array processing
In the C Programming Language, an array is a fixed sequenced collection of the element of the same data types. An array can be used to represent a list of number(int) or name (string) or other data type of similar elements. It is one of the ways of the grouping of similar types of data of single variables names.
Three types of arrays in C programming language
1. One dimensional array
2. Two-dimensional array
3. multidimensional array
Two dimensional Array
Declaration of Two dim Array
Syntex
retuen_type Array_name[size][size];
Example
int marks[4][6]; char alphabat[3][4];
This declare is a 2-dimensional array in c have 4 rows and 6 columns
Initializing 2 dim Array
Initializing-using standard method
Syntax
array_name[row_index][column_index]=value;
Example
arr[0][0]=65; //first element of an array
number 65 placed to address of arr[0][0]
Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[2][3];//declaration of 2 D array
//initializing using stranded method
marks[0][0]=23;
marks[0][1]=33;
marks[0][2]=56;
marks[1][0]=76;
marks[1][1]=58;
marks[1][2]=37;
//display element
printf("Here, student marks\n");
printf("%d\n",marks[0][0]);
printf("%d\n",marks[0][1]);
printf("%d\n",marks[0][2]);
printf("%d\n",marks[1][0]);
printf("%d\n",marks[1][1]);
printf("%d\n",marks[1][2]);
printf("End program!\n");
getch();
return 0;
}
The above code is executed, it produces the following result

Initilaize during the declaration
int marks[4][6]={
{50,71,42,53,36,58} // initialize for row index by 0
{96,68,93,46,32,21} // initialize for row index by 1
{40,71,62,73,57,70} // initialize for row index by 2
{30,11,22,33,47,100} // initialize for row index by 3
};
different way to initialize 2 dim Array
int marks[2][3]={{50,46,57}{78,63,84}}
float height[ ][3]={{124.5,146.8,157.3}{178.9,163.0,154.6}}
Example 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int array[4][4]={
{10,34,56,74},
{400,674,946,604},
{40,64,96,64},
{440,684,936,614}
};
int i,j;
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<4; j++)
{
printf(“array[%d][%d]:%dn”,i,j,array[i][j]);
}
}
return 0;
}
Initialize and display using loops
Initialize and display elements using for loop
Example 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int arr[3][3];
//2D array declaration
int i,j;//counter variable for the for loop
printf("Enter the value for 2 D array\n");
for(i=0; i<=2; i++){
for(j=0; j<=2; j++){
printf("Enter the value for arr[%d][%d]: ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);
//store the entered elements to array
}
}
//Displaying array element
printf("\nYour entered values here\n");
for(i=0; i<=2; i++){
for(j=0; j<=2; j++){
printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
getch();
return 0;
}


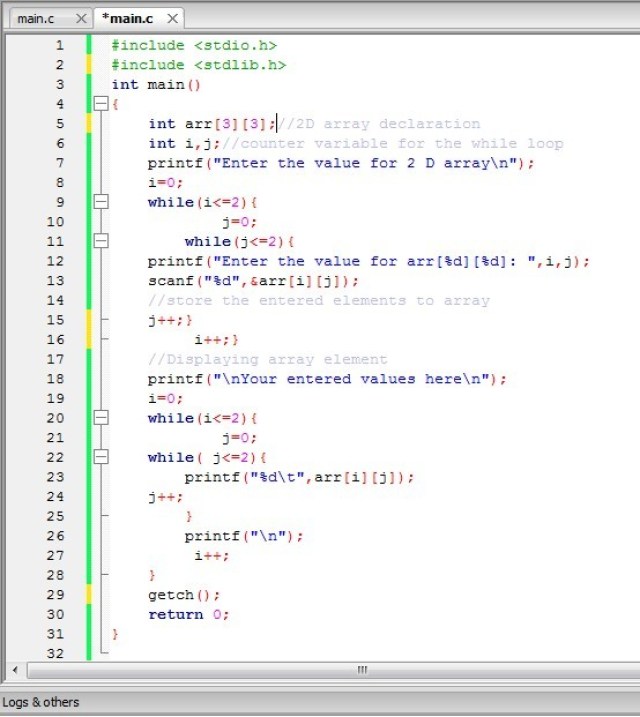
Initialize and display elements using the while loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int arr[3][3];
//2D array declaration
int i,j;//counter variable for the while loop
printf("Enter the value for 2 D array\n");
i=0;
while(i<=2){
j=0;
while(j<=2){
printf("Enter the value for arr[%d][%d]: ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);
//store the entered elements to array
j++;
}
i++;
}
//Displaying array element
printf("\nYour entered values here\n");
i=0;
while(i<=2){
j=0;
while( j<=2){
printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]);
j++;
}
printf("\n");
i++;
}
getch();
return 0;
}
Program
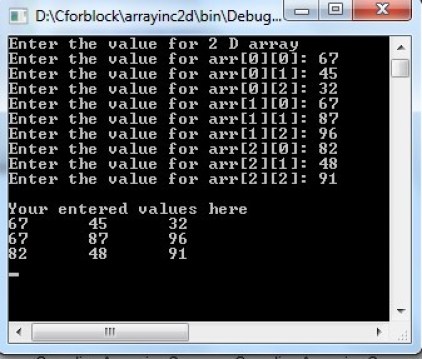
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result
Initialize and display elements using the do-while loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int arr[3][3];//2D array declaration
int i,j;//counter variable for the do-while loop
printf("Enter the value for 2 D array\n");
i=0;
do{
j=0;
do{
printf("Enter the value for arr[%d][%d]: ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);
//store the entered elements to array
j++;}while(j<=2);
i++;}while(i<=2);
//Displaying array element
printf("\nYour entered values here\n");
i=0;
do{
j=0;
do{
printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]);
j++;
}while( j<=2);
printf("\n");
i++;
}while(i<=2);
getch();
return 0;
}
Program

When the above code is executed, it produces the following result

One dim Array in Java One dim Array in C++ One dim Array in C


