Table of Contents
One Dimension Array in Java language
In this tutorial, we will discuss One Dimension Array in Java language
Introduction of Array
The array is a data type in Java, which is the collection of similar type of element that has contiguous memory location, That is similar to a table of an object or primitive data type. We can store an Only fixed set of similar element in java array.
Advantages of java array
- Code optimization – it makes the code optimized, We can retrieve or short the data easily
- Random access – We can get any data located any index position
- It is used to represent multiple data items of similar type by using a single name
- It can be used to implement other data structure similar Stacks, queues, Linked list, trees, graphs
Disadvantages of java array
- Size limit: We can store the fixed-size element in the array, It doesn’t increase in runtime
- Since the array is a fixed size. if we allocate more memory than requirement then the memory space will be wasted
- must be known in early that how many elements are to be stored in the array
- Single Dimensional Array
- Multi-Dimensional Array
Multi-Dimensional Array
- Two Dimension Array
- Three Dimension Array
Array in java is index-based, the first element is stored at 0 indexes of the array,
Array declaration, creation, initialization
Declaration of single Dimension Array in Java
When using an array in a program, you must declare a variable to reference the array
You must specify the type of array when the variable can reference
Syntax
dataType[] array_name;
dataType []array_name;
dataType array_name[];
example
int[] number;
int []number;
int number[];
double[] zscore;
double []zscore;
double zscore[];
String[] name;
String []name;
String name[];
The default value of an array in Java
When we array is declared, the array will be filled by 0 of every array index in the memory location
The default value is zero for numeric type
the default value of the string “null”
the default value of boolean”false”
Example
In this program, when we declare a one-dimensional array in java language(not initialized), Every array index is filled by zero – zero is a default value for integer data type
class ArrayDefaultValue{
public static void main(String args[]){
int[]marks=new int[10];//array is declared
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
System.out.println("value of array index "+i+" is :"+marks[i]);
}
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output
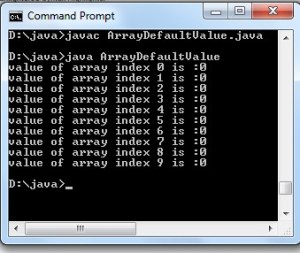
Creation of single Dimension Array in Java
arrayname=new datatype[array length];
Example
number=new int[4];
Diclaration and Creation in one line
Syntax
datatype []arrayname=new datatype[array length];
Example
int [] number=new int[4];
initialization of single Dimension Array in Java
- initialization – using the standard method
here, we can initialize the array element to each cell at a time
initialize one by one
Array
program 1 – int array
class Array2{
public static void main(String []args){
int[] x; //Declaration of single Dimention Array in Java
x=new int[5]; //Creation of single Dimention Array in Java
//initialitation of single Dimention Array in Java
x[0]=10; //..first element
x[1]=5;
x[2]=7;
x[3]=8;
x[4]=22; //fifth element
System.out.println (x[4]); //Display the element index of 4
}
}
out put 22
When the above code executed it produce following output
2. initialization – During the declaration
Syntax
type[]arrayName={List of element seperated by comma};
Example
char[]alphabets={a,b,c,d,e,f,g};
Program 1
class Array_SumAvg{
public static void main(String args[]){
double height[]={67.5,87.6,98.1,56.0,45.54,98.97,77.34,43.5,35.7,51.43};
double sum=0;
for(double h:height)
sum+=h;
double avg=sum/10;
avg=sum/10;
System.out.println("Average height of 10 student :"+avg );
}
}
When the above code executed it produce following output
Average height of 10 student :66.168
initialization and retrieve elements- using loops with Scanner class
Using for loop
Initialize element using for loop(code segment)
for(i=0; i<array.length; i++){
array.length[i]=myObj.next.Int();
}
display of element using for loop(code segment)
for(i=0; i<array.length; i++){
System.out.print(arrName[i]+" ");
}
Program
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayWithFor1{
public static void main (String args[]){
int arr_Len;
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Array length: ");
arr_Len=scan.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[arr_Len];
System.out.print("\nEnter "+arr_Len+" Element to array: \n");
for(int i=0; i<arr_Len; i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("\nDisplay element from array\n");
for(int i=0; i<arr_Len; i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output

Using while loop
Initialize element using while loop(code segment)
i=0;
while(i<array.length){
array.length[i]=myObj.next.Int();
i++;
}
display element using while loop(code segment)
i=0;
while(i<array.length){
System.out.print(arrName[i]+" ");
i++;
}
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayWithWhile1{
public static void main (String args[]){
int arr_Len;
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Array length: ");
arr_Len=scan.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[arr_Len];
System.out.print("\nEnter "+arr_Len+" Element to array: \n");
int i=0;
while(i<arr_Len){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
i++;
}
System.out.print("\nDisplay element from array\n");
i=0;
while(i<arr_Len){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
i++;
}
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output
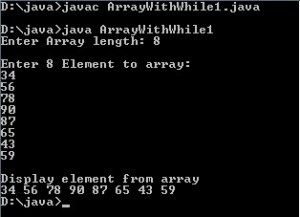
Using the do-while loop
Initilize element using do-while loop(code segment)
i=0;
do{
array.length[i]=myObj.next.Int();
i++;
}while(i<array.length);
display element using do-while loop(code segment)
i=0;
do{
System.out.print(arrName[i]+" ");
i++;
}while(i<array.length);
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayWithDoWhile1{
public static void main (String args[]){
int arr_Len;
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Array length: ");
arr_Len=scan.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[arr_Len];
System.out.print("\nEnter "+arr_Len+" Element to array: \n");
int i=0;
do{
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
i++;
}while(i<arr_Len);
System.out.print("\nDisplay element from array\n");
i=0;
do{
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
i++;
}while(i<arr_Len);
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output

Using Enhanced for loop – retrieve elements from the array
for(int x:arr){
System.out.print(x+" ");
}
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayWithForEach1{
public static void main (String args[]){
int arr_Len;
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter Array length: ");
arr_Len=scan.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[arr_Len];
System.out.print("\nEnter "+arr_Len+" Element to array: \n");
for(int i=0; i<arr_Len; i++){
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("\nDisplay element from array\n");
for(int x:arr){
System.out.print(x+" ");
}
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output
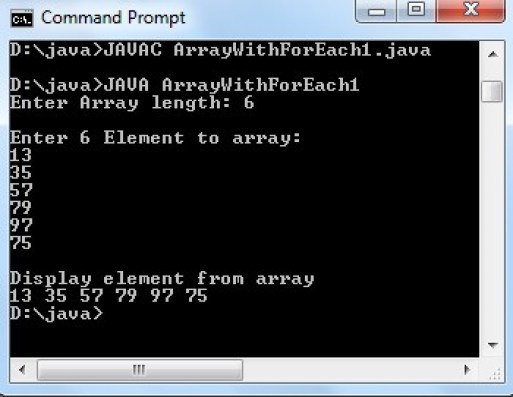
Examples
program 1-
display one d array element using single for loop
class Array3{
public static void main(String []args){
int[] x;
x=new int[5];
x[0]=10;
x[1]=5;
x[2]=7;
x[3]=8;
x[4]=22;
for(int i=1; i<=5;i++){
System.out.println (x[i]);
}
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output
5
7
8
23
Program 2
display one d array element using single Enhanced for loop
class Array3{
class array_foreach{
public static void main(String []args){
int[] x;
x=new int[5];
x[0]=10;
x[1]=5;
x[2]=7;
x[3]=8;
x[4]=22;
for(int i:x){
System.out.println (i);
}
}
}
Program 3
class Arraydemo{
public static void main(String []args){
int[] anArray;
anArray=new int[10];
anArray[0]=100;
anArray[1]=200;
anArray[2]=300;
anArray[3]=400;
anArray[4]=500;
anArray[5]=600;
anArray[6]=700;
anArray[7]=800;
anArray[8]=900;
anArray[9]=1000;
System.out.println(“Element at index 0:”+(anArray[0]));
System.out.println(“Elemeny at index 1:”+(anArray[1]));
System.out.println(“Element at index 2:”+(anArray[2]));
System.out.println(“Elemeny at index 3:”+(anArray[3]));
System.out.println(“Element at index 4:”+(anArray[4]));
System.out.println(“Elemeny at index 5:”+(anArray[5]));
System.out.println(“Element at index 6:”+(anArray[6]));
System.out.println(“Elemeny at index 7:”+(anArray[7]));
System.out.println(“Element at index 8:”+(anArray[8]));
System.out.println(“Elemeny at index 9:”+(anArray[9]));
}
}
When the above code executed it produces the following output
Similar post
One dimArray in Java One dim Array in C++ One dim Array in C
Two dim Array in Java Two dim Array in C++ Two dim Array in C
Three dim Array in Java Three dim Array in C++ Three dim Array in C




